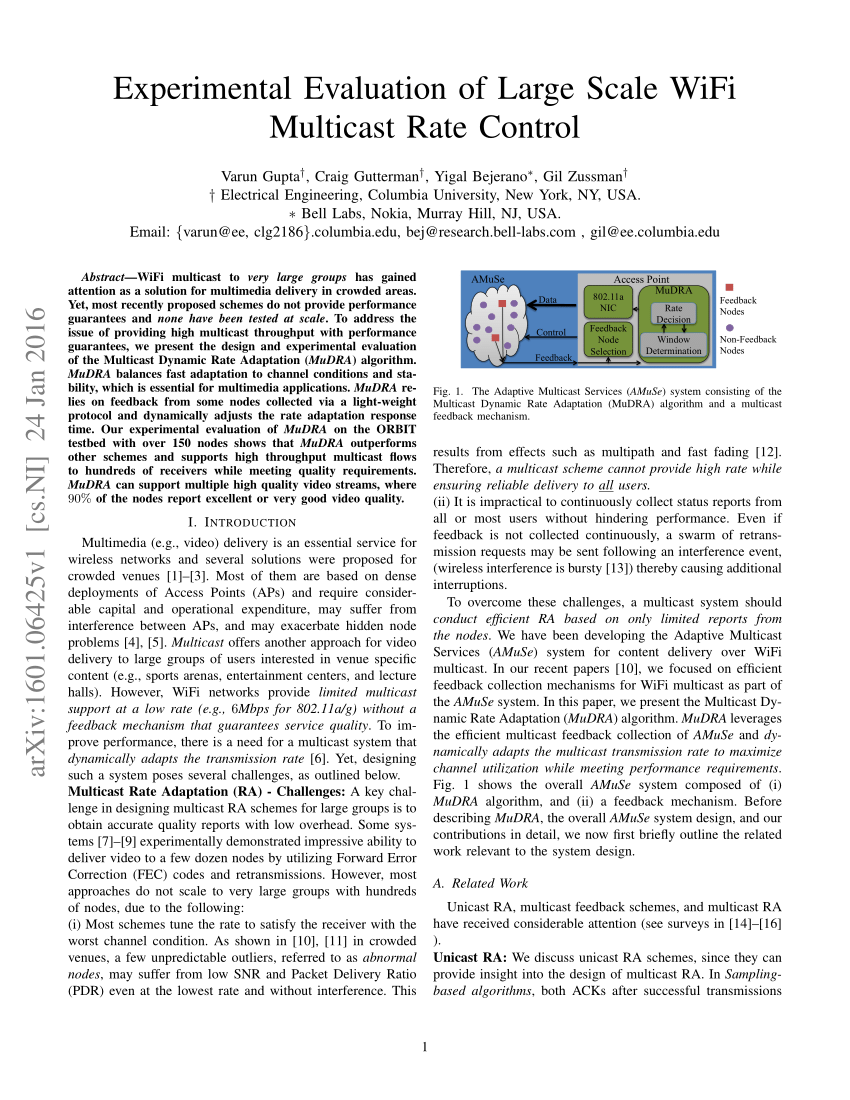
-
Hlbp: A Hybrid Leader Based Protocol For Mac

- The first one is called SEQ driven Leader Based Protocol (SEQ-LBP), in which a. The other reliable MAC layer multicast protocol is called Hybrid LBP (HLBP).
- Admitted students receive a first rate, research-oriented education in. In this thesis, we focus on MAC layer reliable multicast ap. Protocols, SEQ driven Leader Based Protocol (SEQ-LBP) and Hybrid Leader Based Protocol. Ming probabilities and the performances of SEQ-LBP and HLBP based on theoretical.
Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) over IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs, which are considered today as the de-facto wireless access network for local distribution (home networks, hotspots), brings forth a big challenge to guarantee high quality multicast/broadcast delivery over unreliable and time-variant wireless channels. However, in IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs, current standard MAC layer protocols do not provide any error correction scheme for broadcast/multicast.
西安交通大学学报 (未开通), 2009. [22], HLBP: a hybrid leader based protocol for MAC layer multicast error control in wireless LANs. Global Telecommunications.
In our previous work, we enhanced a Leader Based Protocol (LBP) and proposed a Beacon-driven Leader Based Protocol (BLBP) for the MAC layer multicast error control. However, as pure Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) schemes, both LBP and BLBP are not efficient for large multicast groups. In this paper, we combine BLBP and packet level Forward Error Correction (FEC) and propose a Hybrid Leader Based Protocol (HLBP) for the MAC layer multicast error control.
HLBP transmits the original data packets using raw broadcast and retransmits parity packets using an improved BLBP which is bas. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) In order to meet very low packet loss rate (PLR) requirements under strict delay constraints for IP based DVB services over wireless home networks (WHN), an optimized real-time transport protocol (RTP) level hybrid error correction (HEC) scheme is proposed in this paper. The scheme is compared with the Adaptive Forward Error Correction (AFEC) scheme using Reed-Solomon code. By the HEC scheme, the needed redundancy information (RI) for repairing missing packets can be minimized, especially in DVB systems with a single user. The result of quantitative analysis shows that the needed RI of the proposed scheme can even achieve the Shannon limit with only three retransmission rounds.
On the other hand, our studies show that the performance of the HEC scheme is better than that of the AFEC scheme if both the average link PLR and group size are small. However, if both the average link PLR and group size are large enough, the AFEC scheme performs better than the HEC scheme. At last, the simulation results for one typical scenario are also prov. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) Visual CAPCTCHAs, like gimpy images, are commonly used to screen human users from automated computer scripts.
We propose using them for direct, visual authentication of digital documents. The basic assumption is that if it is hard or impossible for the computer to recognize a document, then it cannot manipulate it. If such a document is still recognizable by a human, he or she can be confident that it is authentic, or at least that no automated process has manipulated it. Such authentication is highly desirable in the context of digital signatures, which, due to the computational complexity, have to be produced by a computer. It can be a specialized, trusted cryptographic computer, e.g.
A smartcard, but the path to it is generally not secure. Visual CAPTCHAs can be used for securing the path without the need for additional hardware. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) Media-based services often require a multicast-enabled transport that guarantees quasi error free transmission under strict delay constraints. In packet based networks, furthermore, both multicast and delay constraints deeply influence the architecture of erasure error recovery. Therefore, we propose a general architecture and study its optimization in this paper.
Since the Gilbert-Elliot (GE) erasure error model has been proven to be valid for a wide range of packet based wireless networks, in this paper, we present the generalized architecture and its optimization based on the GE channel model. The architecture integrates nearly all existing erasure error recovery techniques: Automatic Repeat Request, Forward Error Correction and Hybrid ARQ techniques.
Through the optimization, the total needed redundancy information can be minimized by choosing the best scheme automatically among the entire schemes included in the architecture. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) In this paper, an application layer hybrid error correction scheme with Reed-Solomon (HEC-RS) code is proposed to satisfy the very low packet loss ratio (PLR) requirement under a strict latency limit for DVB services over wireless LANs. The PLR performance of the HEC-RS scheme is analyzed and compared with the HEC scheme based on the packet repetition (HEC-PR) technique and an adaptive forward error correction (AFEC) scheme based on RS codes. It is found that the needed redundancy information (RI) of the HEC-RS scheme is much less than that of the AFEC scheme. However, if the group size and link PLR are small enough, the needed RI of the HEC-RS scheme is proven to be much more than that of the HEC-PR scheme. As a result, the optimum performance can be achieved when combining the HEC-PR and the HEC-RS scheme. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) In Wireless LANs MAC layer multicast error control schemes lead to shorter delays compared with application layer schemes. Asus x53s support.
In this paper, we enhance a Leader Based Protocol (LBP) and propose a Beacon-driven Leader Based Protocol (BLBP) for the MAC layer multicast error control. Like LBP, BLBP selects one of the multicast group receivers as the leader and allows acknowledgement and negative acknowledgements from the leader receiver and non-leader receivers respectively. The use of the beacon frame is to lead the non-leader receivers to set timers and to announce the sequence number of the following data frame.
Thanks to the sequence check based on the beacon frame, BLBP avoids the unnecessary transmissions in LBP. Burlington girls always crying for mac. Both the theoretical analysis and simulation experiments show that BLBP can correct nearly all the errors for all receivers in the MAC layer and is more efficient than LBP. BLBP is even more efficient than the application layer automatic repeat request (ARQ) scheme and the total multicast delay is much shorter.
BLBP is very g. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) In wireless networks current standard MAC layer protocols don’t provide any error correction scheme for broadcast/multicast. In this paper, we enhance a Leader Based Protocol (LBP) and propose a Beacon-driven Leader Based Protocol (BLBP) for the MAC layer multicast error control. To guarantee a very low Packet Loss Ratio (PLR) under strict delay constraints for video multicast over a Gilbert-Elliott (GE) channel, we analyze BLBP and compare it with LBP and different application layer multicast error control schemes via simulation experiments. Both the theoretical analysis and simulation results show that BLBP can correct nearly all the errors for all receivers in the MAC layer and is more efficient than LBP. BLBP is also more efficient than the application layer Automatic Repeat request (ARQ) scheme and the total multicast delay is much shorter. BLBP is very good for real-time multicast applications with strict delay constraints.
Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) In IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs current standard MAC layer protocols do not provide any error correction scheme for broadcast/multicast. In our previous work, we enhanced a Leader Based Protocol (LBP) and proposed a Beacon-driven Leader Based Protocol (BLBP) for the MAC layer multicast error control. In this paper, we combine BLBP and packet level Forward Error Correction (FEC) and propose a Hybrid Leader Based Protocol (HLBP).
Hlbp: A Hybrid Leader Based Protocol For Mac Download

HLBP transmits the original data packets using raw broadcast and retransmits parity packets using an improved BLBP which is based on block feedback. To guarantee the required Packet Loss Ratio (PLR) under strict delay constraints, we analyze HLBP, develop formulas to optimize its performance and evaluate its performance via simulation experiments. Both theoretical analysis and simulation results show that HLBP is much more efficient than LBP and BLBP especially for large multicast groups and is even more efficient than the best application layer multicast error correction scheme. Estimated H-index: 10 (Saarland University) Leader-based protocols have been proposed for wireless networks such as 802.11 as an alternative approach to MAC layer ARQ. If based on feedback cancellation, such protocols may achieve low latency and high throughput at predictable reliability and superior scalability with respect to the number of subscribers. Especially for delay-bounded multicast A/V transmission these properties are highly desirable.
The authors have proposed such schemes to the IEEE task group TGaa, which is dedicated to introducing more reliable multicast to 802.11 wireless LANs. This paper provides results on wireless feedback cancellation probabilities derived from real measurements with consumer hardware as well as simulation data.
Estimated H-index: 5 (Saarland University). More Internet protocol (IP) based media delivery enables applications such as Voice over IP or, most recently, stereoscopic HD-TV. Suchlike transport of typically time-constrained media between two end-points has a number of important characteristics, both on the transport and content side. We focus on live streams of audio-visual data that are assumed as time-constrained and loss-tolerant.
We aim at optimizing IP transport over heterogeneous networks by hybrid and loss domain separated error correction with residual error. Hybrid error correction (HEC) approaches the channel capacity dynamically and achieves predictable reliability and predictable delay (PRPD) when residual loss is tolerable, while loss domain separation applies optimally chosen HEC parameters to individual network segments. In this paper, we apply an atomic HEC coding unit to individual segments of network links between source and sink, and show by analysis and example how redundancy is distributed optimally.